Announcement of ‘comprehensive drug management plan’… Expansion of ‘non-consent full body scanning’ to all airports
In order to detect small amounts of drugs hidden in clothes, the government will introduce ‘millimeter wave personal scanners’, a scanning device that can quickly examine the entire body without individual consent, at all airports across the country next year.
In addition, it was decided to more than double the testing rate for incoming travelers, including resuming full testing of travelers entering the country from areas with frequent drug crimes.
In particular, we plan to block the smuggling of drugs at the border stage by moving up the time of full inspection to before entry screening and conducting cabin baggage and personal inspection immediately after disembarking from the flight.
The government held the 7th Narcotics Countermeasures Council at the Seoul Government Complex on the 22nd, and after the meeting, related ministries jointly announced a ‘comprehensive drug management plan’ including the above.
This measure consists of three major areas and nine implementation tasks, including ▲concentration and crackdown on illegal drugs, ▲reorganization of the medical drug management system, and ▲expansion of treatment, rehabilitation, and prevention infrastructure.
◆ Intensive crackdown on illegal drugs
Since most domestic drug seizures originate from overseas smuggling, blocking drug smuggling at the border stage is of utmost importance.
Accordingly, the government will more than double the testing rate for incoming travelers and, starting in November, advance the timing of all testing for travelers from countries with high crime rates from after entry screening to before, and conduct inspections of their carry-on baggage and personal information as soon as they get off the flight.
The inspection system for international cargo, such as express cargo and international mail, will also be improved. Cargo from high-risk countries will be separated from general cargo and intensively inspected, and the number of inspections for mail from high-risk countries will be increased by more than 50%.
To this end, we plan to operate the Drug Smuggling Special Countermeasures Promotion Team, an organization dedicated to cracking down on smuggling, to respond systematically and organically through customs clearance and surveillance, drug smuggling investigation, and support of cutting-edge equipment.
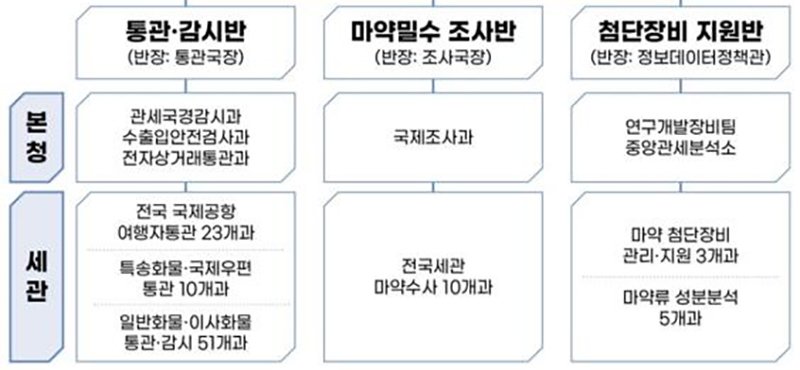
Drug Smuggling Special Measures Promotion Team (Head: Deputy Director of the Korea Customs Service)
Based on close cooperation between investigative agencies, including regular and frequent cooperation between the drug investigation working councils of 17 cities and provinces across the country, centered around the Drug Crime Special Investigation Headquarters, we will respond with all our might through an intensive crackdown system virtually 365 days a year.
In addition, we identify criminal proceeds through cooperation with the criminal proceeds tracking team and actively utilize the confiscation and preservation system before prosecution.
In particular, we plan to build a drug database on drug crime information, such as drug smuggling cases and international smuggling organizations in countries with drug imports around the world, and actively use it for investigations such as smuggling.
In order to strengthen punishment for drug crimes, we plan to strengthen prosecution case handling standards for drug crimes and actively express opinions across government agencies, such as establishing or strengthening punishment for sentencing standards for drug crimes.
Meanwhile, high-resolution and ultra-high sensitivity mass spectrometry that can identify even trace amounts of narcotics will be introduced, and sites for illegal narcotics trafficking and advertising will be quickly detected and blocked through advanced online monitoring.
In addition, we will develop and advance a crime tracking system that tracks the routes of drug offenders through CCTV or predicts and tracks organized crime by analyzing the correlation between drug crime information.
Prior to this, the government has been operating a virtual asset TF team since last October in which drug and cyber investigators participate in provincial and provincial police offices to systematically respond to virtual assets used in drug crimes.
◆ Reorganization of the medical drug management system
Institutionalize the identification of addiction among medical professionals so that medical professionals who are addicted to narcotics do not prescribe narcotics to themselves or their patients.
In addition, if a license is determined to be addicted, the license is revoked, the review standards for re-issuance are strengthened, and the obligation to complete an education program is imposed upon re-issuance.
For ingredients that have social issues, such as propofol or appetite suppressants, the standards for prohibiting prescriptions will be strengthened, such as limiting the amount and number of prescriptions and adding additional ingredients.
In particular, we plan to ensure that the patient’s identity is confirmed to prevent medical narcotics from being prescribed in the name of the deceased or another person, and to check compliance at the hospital site.
By mandating that doctors check the patient’s history of being prescribed or administered medical narcotics at other hospitals, it prevents patients from ‘hit-and-run drug shopping’ and supports appropriate prescriptions.
This policy will be applied starting with fentanyl, a narcotic painkiller, in June of next year, and will be gradually expanded to include propofol and zolpidem in the future.
In addition, although only doctors have been notified that they are subject to suspicion of prescription abuse, patients are also being added to the target range, and the number of warnings will be expanded from twice a year to six times a year (once every two months).
Meanwhile, cases of misuse were extracted by manually analyzing prescription and medication details in the integrated narcotic management system, but in the future, automatic detection and analysis and extraction of violation cases will be promoted through artificial intelligence (AI) intelligence.
This system is linked to various public information, and through AI algorithm learning, it automatically detects and analyzes prescription and medication details even if there is no clear violation of abuse standards, automatically extracts suspicious cases and conducts detailed analysis.
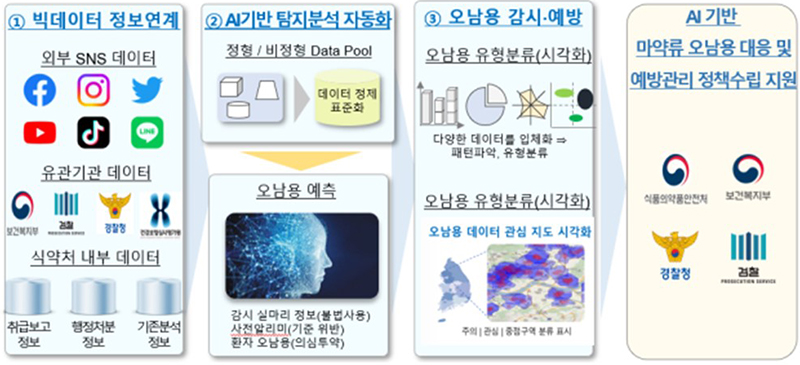
AI-based information/collection analysis visualization and policy development
For suspicious cases, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety conducts monthly pan-ministerial planning and joint inspections with the prosecution, police, welfare, and local governments.
If it is determined to be a violation of misuse, an investigation will be requested and commenced immediately. In particular, the scope of special judicial police duties will be expanded to include drug handlers (excluding marijuana growers), and a medical drug investigation task force (tentative name) will be operated to strengthen inspection and crackdown capabilities.
Accordingly, medical professionals and patients who abuse will be severely punished, administrative measures such as suspension of work due to misuse will be limited to conversion to fines, and improvements to the fine imposition system and introduction of punitive fines will also be promoted.
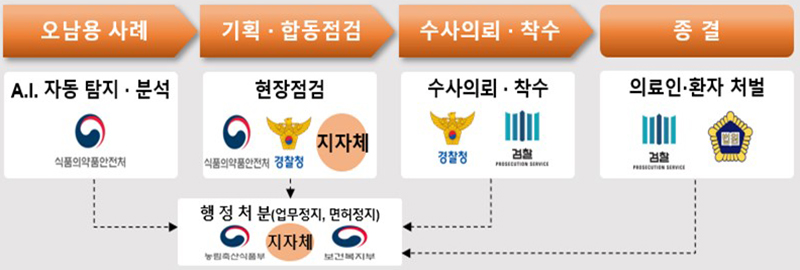
Medical drug management system
◆ Expansion of treatment, rehabilitation, and prevention infrastructure
The recidivism rate for drug crimes reaches 36%, which is 1.5 times higher than that for other crimes. In particular, people in their 30s or younger account for more than half of all drug offenders.
Therefore, it is important to expand treatment and rehabilitation infrastructure in order for addicts to avoid falling back into crime and return to being healthy members of society.
Accordingly, the government decided to expand treatment and protection institutions to strengthen the role of drug addiction treatment in each region and to provide support such as operating expenses, performance compensation, and environmental improvement when necessary to revitalize operation.
By applying health insurance to those subject to treatment protection, more addicts will receive appropriate treatment, timely payment of treatment fees to treatment and protection institutions will be made, and considering the fact that treatment is more difficult than mental illness, the number of drug addiction treatments will be improved.
In particular, the addiction rehabilitation center currently operating in three locations in Seoul, Busan, and Daejeon will be expanded to 17 locations across the country next year, and a 24-hour counseling call center will be operated from March next year to provide helpful rehabilitation support anytime, anywhere.
In January next year, Hwaseong Vocational Training Prison and Busan Prison will be officially designated and operated as correctional facilities dedicated to the rehabilitation of drug offenders, and will be further expanded to four major regions, including Seoul, Daegu, Daejeon, and Gwangju, during the first half of next year.
In addition, we plan to develop and operate an integrated course, a program to help drug offenders recover, and expand the operation of healing programs for youth.
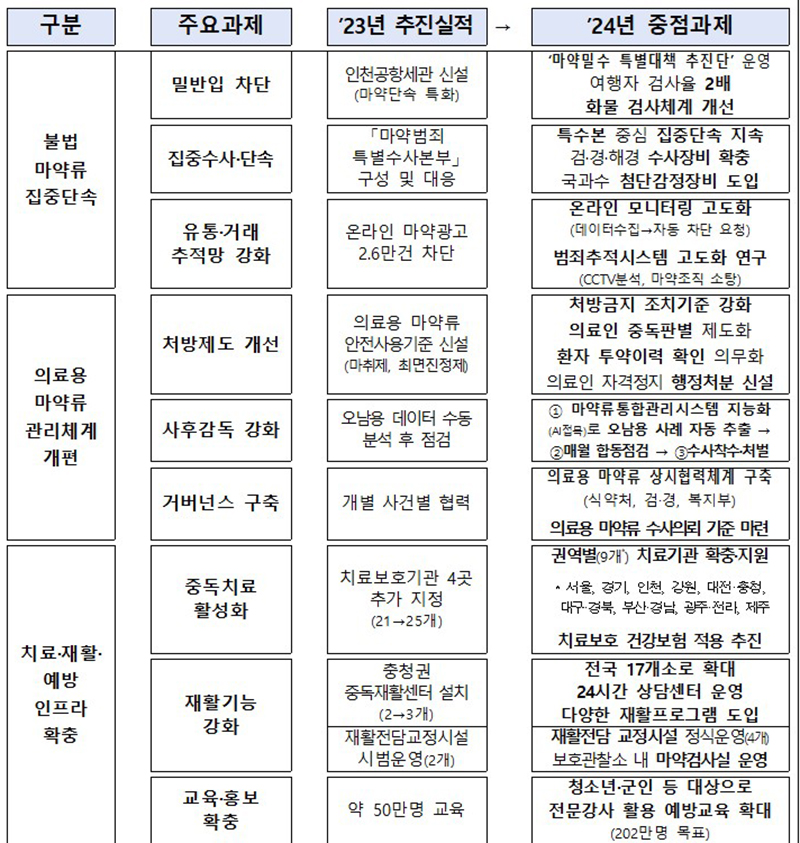
The changes in 2024
Bang Ki-seon, Director of the Office for Government Policy Coordination, said, “As a result of all ministries’ all-out response to the spread of narcotics, visible results were achieved, such as the crackdown on 20,230 drug offenders and the seizure of 822.7 kg in the first 9 months of this year, an increase of 48% and 45%, respectively, compared to the same period last year. “It’s showing,” he said.
He continued, “We reiterate that the government will do its best to respond to the spread of narcotics by allocating next year’s budget for narcotics response to KRW 60.2 billion, which is 2.5 times larger than this year’s budget.” “We will do our best to prevent people from accessing drugs,” he emphasized.
Source: Policy news, link


Comments