Announcement of the 2nd Comprehensive Plan for Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Management… Designation of additional regional centers
A ‘human network’ that supports the treatment cooperation system of specialists in the region will be introduced on a pilot basis from January next year so that patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as acute myocardial infarction can keep the golden time for treatment.
In addition, regional cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease centers currently operating in 14 regions will be sequentially expanded and designated for 24 regions, and the National Cardiovascular Research Institute, which is affiliated with the National Institute of Health, will also be established.
Relevant ministries such as the Ministry of Health and Welfare and the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced the 2nd Comprehensive Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Management Plan (2023-2027), including these contents, at the 27th Ministerial Meeting on Current State Affairs presided over by the Prime Minister.
The Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Management Comprehensive Plan is established every 5 years to comprehensively and systematically manage cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, which are a major cause of death in Korea and cause personal pain and social loss due to their high disease burden and severity.
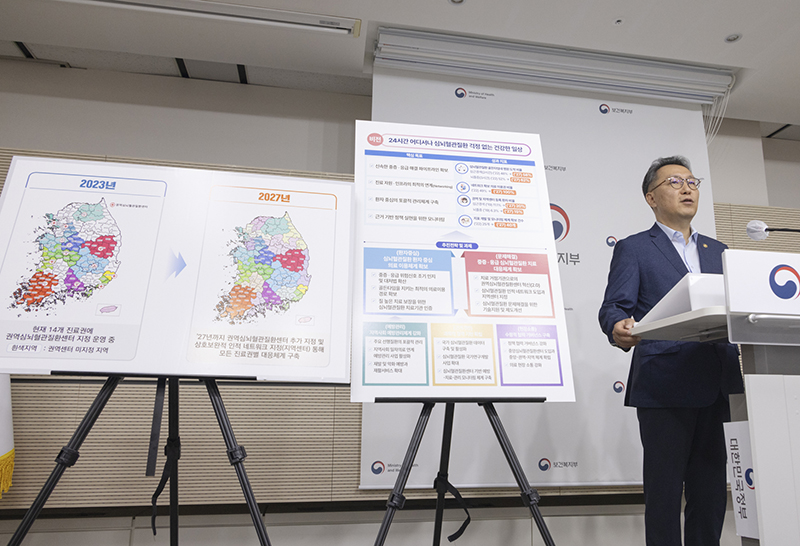
Second Vice Minister of Health and Welfare Park Min-soo announces the 2nd Comprehensive Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Management Plan at the Government Complex Sejong in Sejong City on the morning of the 31st. (Photo = Ministry of Health and Welfare)
The number of patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in Korea is about 2.9 million annually, and the annual medical expenses are approaching 7 trillion won, which is continuously increasing due to the aging population.
However, death can be prevented if properly treated within the golden time, and emergencies can be prevented if the usual preceding diseases are well managed.
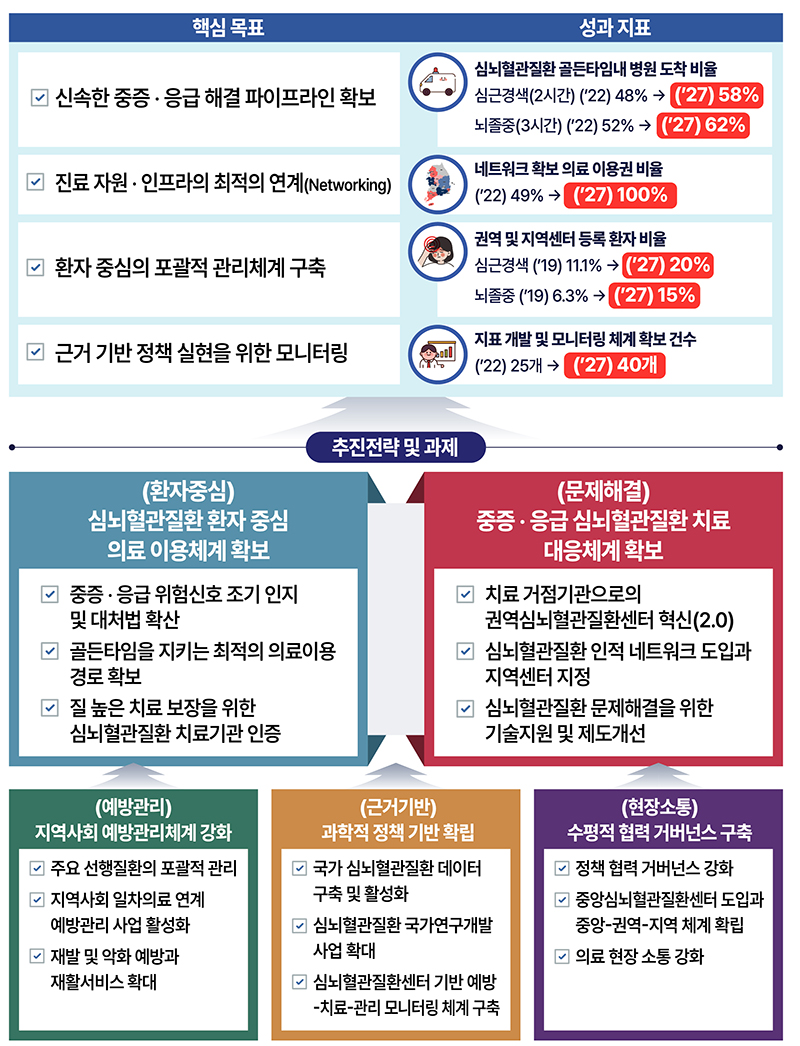
Accordingly, the government prepared the second comprehensive plan to respond to the entire cycle of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, including prevention, treatment, and management, and prepared 5 promotion strategies and 15 key tasks with the vision of a healthy daily life without worrying about cardiovascular disease 24 hours a day, anywhere.
◆ Securing patient-centered medical use system
Cardiocerebrovascular disease, which has a golden time, determines life or death by coping with it in the early stages, so the ability of patients and their families to respond is very important.
Accordingly, it was decided to strengthen education and publicity so that patients and their families can quickly recognize emergency symptoms and respond appropriately.
In addition, it plans to increase awareness of risk signals and symptom recognition education such as self-monitoring support, promote response rules for each symptom and emergency situation, and operate a cardiovascular disease information center.
In addition, the cardio-cerebrovascular disease medical use area is analyzed every three years, and the current status of treatment hospitals in residential areas within the golden time is provided in a map format that is easy for patients to understand.
In particular, the cardiocerebrovascular disease medical use map is planned to be provided to 119 ambulances and emergency medical institutions nationwide and used for education to help understand the trend of patients’ medical use and changes in treatment resources.
It plans to operate a hotline for patients in the high-risk group through regional and regional cardiovascular disease centers to guide the optimal medical use route within the golden time, such as quick decision to visit the hospital and support for public transportation when visiting the hospital.
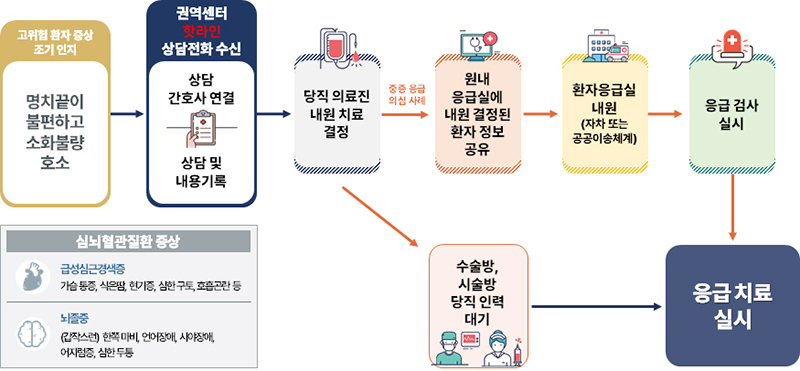
◆ Securing severe/emergency treatment response system
The Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Centers currently designated and operated in 14 regions across the country will be reorganized into an integrated base institution for the entire cycle of prevention, treatment, and management of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases equipped with comprehensive professional treatment capabilities in internal and surgical departments.
To this end, a three-year cycle evaluation will be conducted, including criteria for not only preventive management business capacity but also treatment capacity, and re-designation will be decided.
As a result of the evaluation, it is difficult to re-designate, but the type of regional center operation will be diversified, such as designating it as a fostering regional center according to the decision of the Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Management Committee for regions with weak medical infrastructure.
In addition, as a result of analyzing the cardiocerebrovascular disease medical use area, considering the 24 areas derived from the patient demand side, the current 14 regional centers are planned to be sequentially expanded and designated.
On the other hand, the burnout and departure of specialists due to the burden of severe and emergency response in the field of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases will be alleviated, and prompt transfer decisions will be made for diagnosis and surgery/procedures of emergency patients.
In particular, to shorten the transfer time, a cardiovascular disease human network that supports a treatment cooperation system of specialists with treatment capabilities will be introduced.
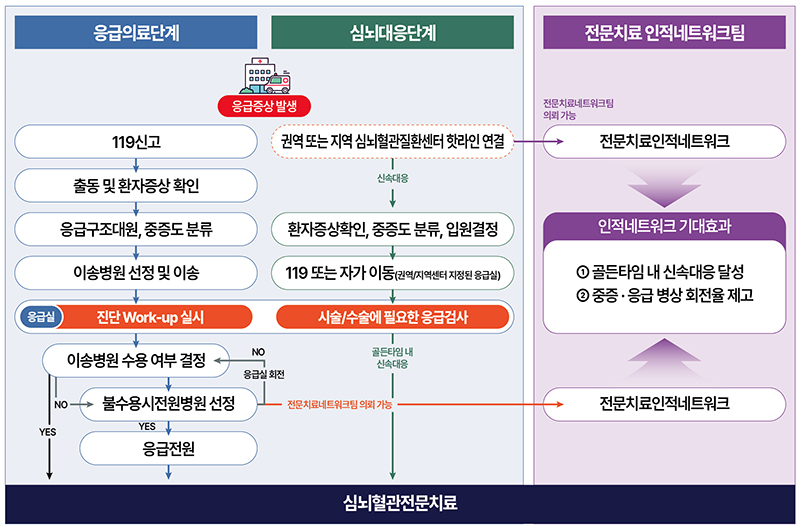
This network consists of at least seven people belonging to different medical institutions within the reachable range within the golden time for each disease and treatment method, such as acute myocardial infarction, stroke, and aortic dissection.
In addition, it aims to provide timely services through prompt decision-making in the process of linking emergency medical care with specialized treatment and specialized treatment.
If the decision of a specialist with treatment competence is made quickly, the emergency medical stage can be shortened, and the problem of non-acceptance by emergency medical institutions can be expected to be alleviated by securing emergency beds.
The human network project is planned to be promoted in the form of a health insurance pilot project that attempts a new team-based compensation system, and the pilot project will be implemented from January next year after preparing detailed project guidelines and selecting participating organizations.
Meanwhile, in order to activate this pilot project, it plans to provide technical support such as a dedicated platform and institutional support such as granting qualifications to apply for regional cardiovascular disease centers.
◆ Reinforcement of community prevention and management system
It promotes patient-centered comprehensive management of chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia, which are major preceding diseases of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
To this end, it plans to prepare criteria for patients to be managed, such as patients with complex chronic diseases, set preventive management goals for each life cycle, and guide customized management methods for each risk factor.
Cardiocerebrovascular disease education and information will be provided in various ways.
In response, it conducts training to strengthen the expertise of local community project managers in cooperation with public health centers, hypertension/diabetes registration management centers, and city and provincial cardiovascular disease prevention and management project support groups.
In addition, it plans to develop and disseminate clinical practice guidelines for primary care institutions and preventive management guidelines for the general public.
The health information provision system will also be improved through campaigns to induce early recognition and continuous management of chronic diseases, vitalization of content distribution reflecting management goals by life cycle, and operation of an informatization platform for providing health information with improved user access convenience.
For those with health risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia as a result of checkups, customized health counseling is provided, and chronic disease management is strengthened through mobile health care at public health centers based on checkup results.
In addition, to strengthen the management of complex chronic diseases, the expansion of dyslipidemia tests within the national health checkup will be reviewed.
In particular, occupational groups with high risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are supported with specialized health examinations and health management programs, and health management technical support is also strengthened for vulnerable workplaces that may be exposed to work-related diseases.
In order to strengthen community-based prevention and management projects, the target areas for the hypertension and diabetes registration management project will be continuously expanded and educational programs will be expanded in cooperation with academic associations in various related fields such as clinical, preventive medicine, nursing, and nutrition.
On the other hand, the primary care chronic disease management project plans to expand the target area to the whole country and prepare plans for linkage with related projects such as hypertension/diabetes registration management project and clinic-level chronic disease management.
Expand and install a wide-area education center so that various projects can be linked and utilized when providing prevention and management training for professional personnel.
In order to meet policy demand for chronic disease management and create patient-centered chronic disease policy conditions, the government, related organizations, and expert councils will be operated, and based on this, mid- to long-term strategies that can cover all chronic diseases will be established.
In addition, by strengthening recovery and maintenance management to prevent complications, recurrence, and aggravation of severe cardiovascular disease, unmet service demand that requires rehabilitation treatment will be identified and based on this, a rehabilitation support model will be developed.
Establishment of regional center-centered rehabilitation services, etc. to increase accessibility, early rehabilitation treatment to minimize the aftereffects and complications of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, preparation of complication diagnosis criteria, clinical treatment guidelines, and monitoring guidelines, and establishment of a management system after discharge of patients with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, etc. Management is also strengthened.
◆ Promotion of policies based on scientific evidence
Establish a nationally approved statistics production system for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction, stroke and related complications.
It produces statistics by country and region, supports policy promotion by developing visualization information production and online statistics provision services, and establishes new data sources through linkage with national surveys, observations, and reported data.
In addition, long-term follow-up (cohort) projects for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and major complications and research resources produced through patient registration projects are planned for data quality management and national data projects to utilize health information development and clinical practice.
In particular, research and development on the entire cycle of prevention, treatment, and management of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases will be expanded, and development of screening tools, management indicators, and risk assessment tools for screening high-risk groups will be promoted.
It will expand technology development for the treatment and management of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, such as advancement of medical treatment technology and minimization of sequelae, and promote the establishment of the National Cardiovascular Research Institute under the National Institute of Health.
Research and development that enhances practicality in the clinical field will also be expanded, such as the spread of prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation means that have been proven effective through research, measures to improve treatment performance, and the development of patient-experienced medical technology based on discovering unmet medical needs.
Establish a nationwide registration system by expanding the stroke and myocardial infarction registry establishment project targeting patients at regional cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease centers.
Meanwhile, in order to promote evidence-based policies, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease monitoring indicators (currently 25) will be expanded and published in the form of an annual data book.
For integrated and systematic data management, we plan to lay the foundation for data business by establishing a cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease information system.
◆ Building horizontal cooperative governance
Strengthen cooperation between the Ministry of Health and Welfare and the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, such as revising laws to promote research and development of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, the Central Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Center and the Central Emergency Medical Center, cooperation between policies for managing chronic diseases, and cooperation between the central and local governments.
For clinical leadership-based policy support, the Central Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Center is introduced to establish a cooperative-based cardiovascular-cerebrovascular disease central-regional-regional delivery system.
In order to strengthen the role of the Cardiocerebrovascular Disease Management Committee for deliberating major issues of cardiovascular disease management and to revitalize its operation, the scope of committee participation is expanded to include representatives of internal and surgical societies, medical associations, hospital associations, and patient groups.
Through this, it plans to implement field-oriented policies by constantly communicating with the medical field in the policy decision-making process.
Second Vice Minister of Health and Welfare Park Min-soo emphasized, “The golden time for cardiovascular disease, which threatens the life and health of the people, begins with the patient’s early recognition and response, and the key is to quickly connect it to severe and emergency professional treatment.”
“In terms of policy, we will focus on tasks to improve the response system for severe and emergency treatment, such as patient-centered prevention and management of the entire life cycle and introduction of human networks,” he said.
He added, “Cardiocerebrovascular disease is a very important field among essential medical care, and we will faithfully implement it with continuous interest so that the achievements of this comprehensive plan can serve as an alternative to solving problems in other essential medical fields.”
Inquiries: Ministry of Health and Welfare Disease Policy Division (044-202-2509) Emergency Medicine Division (044-202-2557) Disaster Medical Division (044-202-2641), Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Chronic Disease Prevention Division (043-719-7436), National Health Research Institute Cardiovascular Disease Research Division (043-719-8665), Fire Administration 119 Ambulance Division (044-205-7631), Ministry of Employment and Labor Occupational Health Promotion Team (044-202-8892)
Ministry of Health and Welfare
Source: Policy news, link

Comments